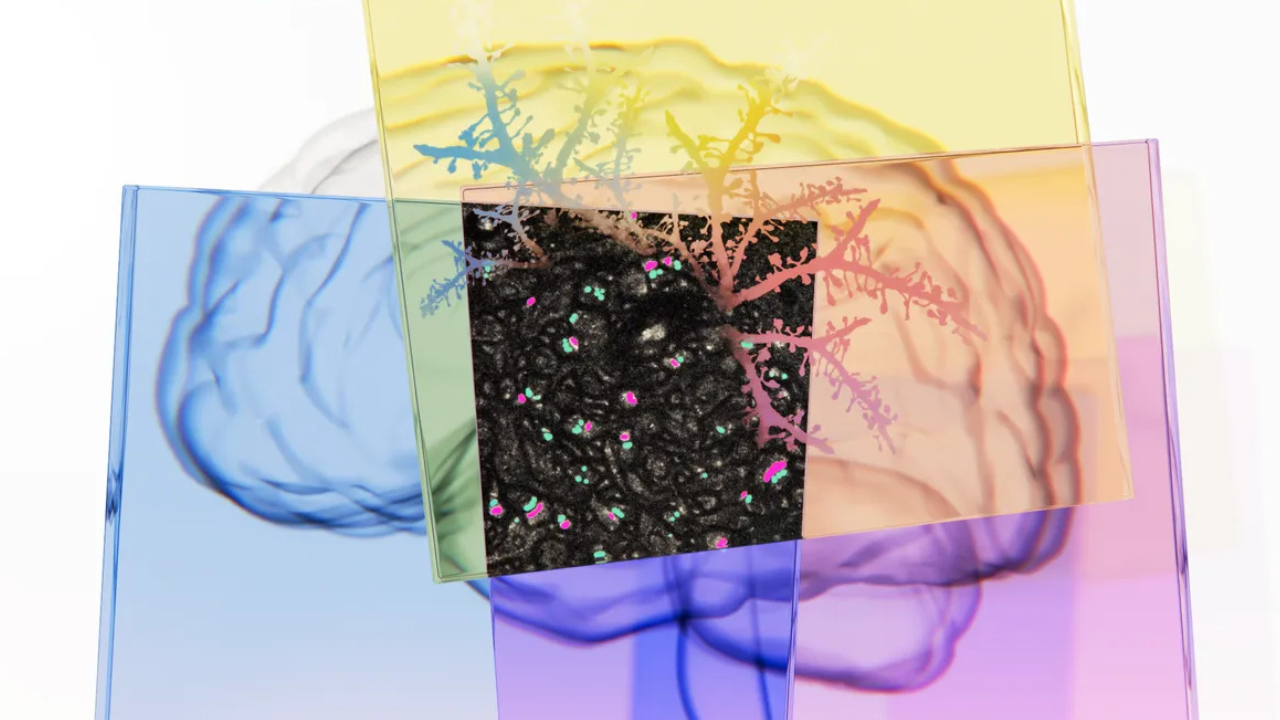
For decades, Google Research has been using AI to precisely map the connections between every cell in the brain in an endeavor called connectomics. Furthering its vision, in collaboration with the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA), Google has been able to map the brain without nanoscale features, like molecules, cells, and their connections.
To achieve this, the collaboration has proven pretty beneficial for the organizations involved in achieving the goal of brain mapping through means like AI and emerging technology. Google has developed a new method for brain mapping, called LICONN, that could make connectomics significantly more accessible.
To read what's happening in technology, Click here!
How’s LICONN helping Google?
LICONN is a protocol that physically expands brain tissue while preserving its structural integrity and simultaneously labels all proteins chemically to enhance image contrast for tracing neurons and identifying cellular structures like synapses.
Google's results matched closely with manual tracing of all the sprawling dendrites and thin, twisty axons within a subsection of tissue.
To read about Kaspersky's latest uncovering of a cyberattack by the infamous Lazarus group on South Korean companies, click here!
What's the significance of this?
This research holds significant promise for making connectomics more accessible and for enabling scientists to extract 'multimodal' connectomes—integrating information about neurons and synapses with previously inaccessible molecular details.
Researchers have so far used LICONN to map mouse brain tissue with the aim of using it for human brains in the future.